Our Speciality Doctors
Orthopaedics
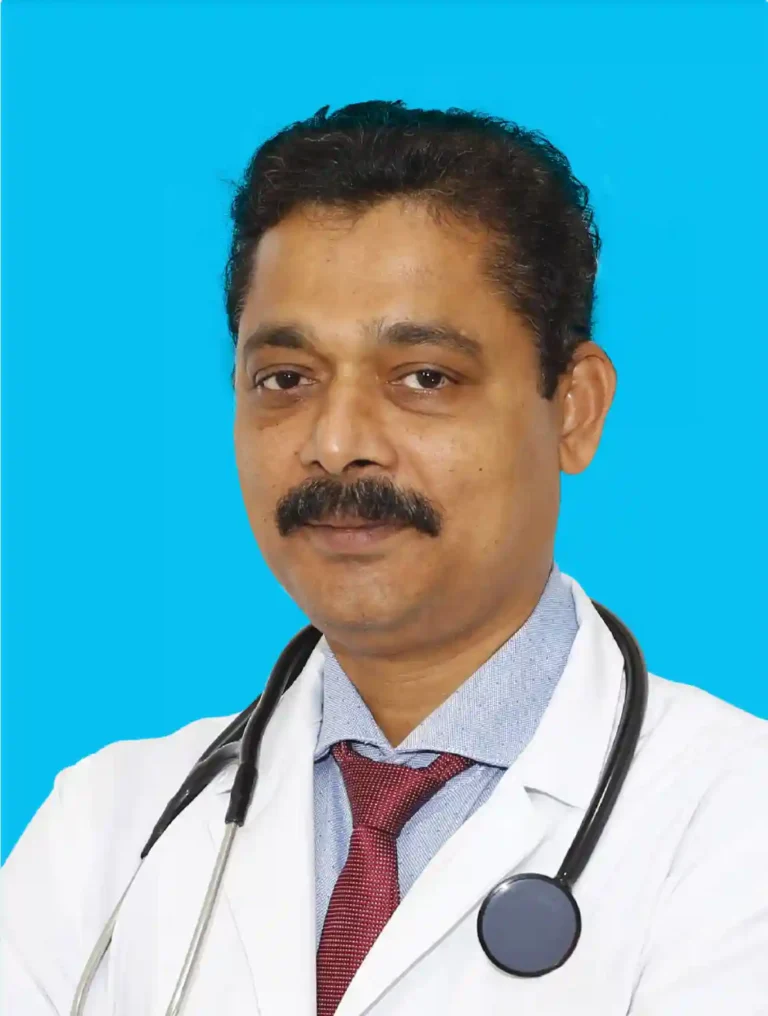

Dr. M. Saleem
Chief Orthopaedic Surgeon

Dr. Prabaharan
Orthopaedician
Our Speciality Doctors
Orthopaedics

Dr. M. Saleem
Chief Orthopaedic Surgeon
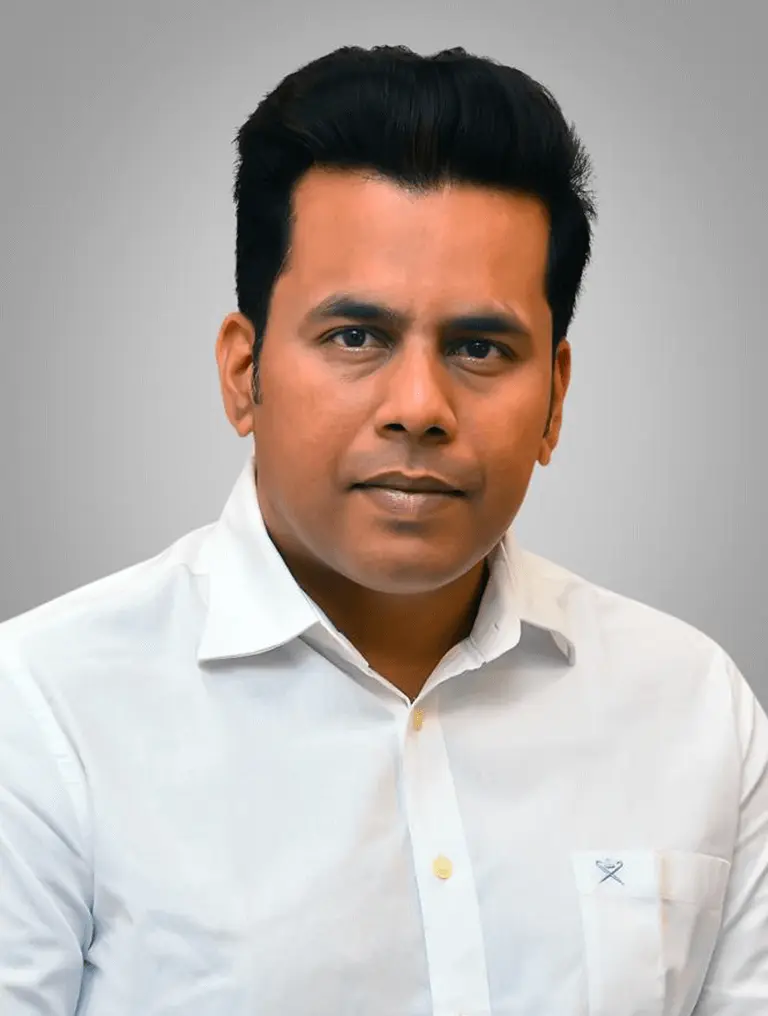

Dr. K. Koushik
Chief Cardiothoracic Surgeon
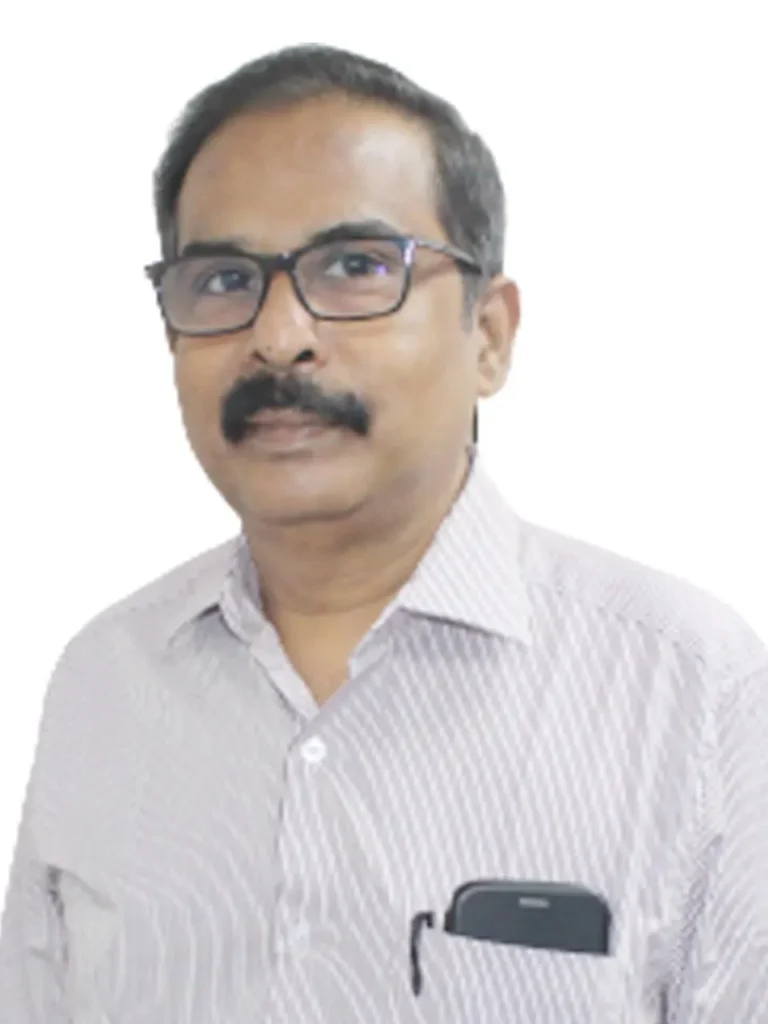

Dr. D. Krupa Shankar
Senior Consultant Neurosurgeon

Dr. Aravind
Cardiologist

Dr. Senthil Kumar
General Physician

Dr. Chithradevi
General Physician

Dr. Indira
Gynaecologist

Dr. Sheeba
Paediatrician

Dr. Arulmozhi
Diabetologist

Dr. Prabaharan
Orthopaedician

Dr. Loganathan
Laparoscopic Surgeon

Dr. Sindhu
Pulmonologist

Dr. A. G. Niza
Emergency Physician

Dr. A. Prakash
Critical Care